Psyche
Table of Contents
1. Systems Breakdown
1.1. 1. Key Components of the Psyche System:
Based on various psychological models (primarily drawing from Freudian and Jungian perspectives, but acknowledging others), the key components of the psyche include:
- Conscious Mind: Thoughts, feelings, and perceptions we are currently aware of.
- Subconscious (Preconscious) Mind: Thoughts and feelings that are not currently in awareness but can be easily retrieved.
- Unconscious Mind: A reservoir of feelings, thoughts, urges, and memories that are outside of conscious awareness. Often a driving force behind behavior.
- Id: The primitive and instinctual part of the mind that contains sexual and aggressive drives and hidden memories. Operates on the pleasure principle, demanding immediate gratification.
- Ego: The realistic part that mediates between the desires of the id and the super-ego. Operates on the reality principle, satisfying the id's desires in ways that are socially acceptable.
- Superego: Incorporates the values and morals of society which are learned from one's parents and others. Controls the Id through guilt and aims for moral perfection.
- Persona: The social face the individual presents to the world. It is a mask that conceals the true self.
- Shadow: The unconscious aspect of the personality that the conscious ego does not identify in itself. It represents the "dark side" of the personality.
- Self: The central archetype that represents the total personality, integrating the conscious and unconscious aspects of the individual.
1.2. 2. Analysis of Relationships and Interactions:
The psyche is a dynamic system where these components constantly interact and influence each other.
- Conscious <-> Subconscious <-> Unconscious: Information flows (sometimes restricted) between these levels of awareness. Unresolved conflicts in the unconscious can manifest in the conscious as anxiety, depression, or other psychological symptoms.
- Id <-> Ego <-> Superego: This is the classic Freudian conflict. The Id demands, the Superego restricts, and the Ego attempts to find a balance and mediate between the two while navigating external reality.
- Persona <-> Shadow: The Persona is often developed as a way to hide or compensate for the Shadow. A healthy psyche involves acknowledging and integrating the Shadow rather than repressing it.
- Ego <-> Self: The Ego is the center of conscious awareness, but the Self is the ultimate goal of integration and wholeness. The process of individuation (Jung) involves aligning the Ego with the Self.
- All components are influenced by past experiences, genetics, social and cultural factors, and the individual's developmental stage.
1.3. 3. Breakdown into Simpler Parts:
To simplify, we can group the components into three core functional areas:
- Awareness: (Conscious, Subconscious, Unconscious) - Deals with information processing and access.
- Motivation/Drive: (Id, Superego) - Deals with the forces that propel behavior.
- Regulation/Mediation: (Ego, Persona, Shadow, Self) - Deals with managing internal conflicts and navigating the external world.
1.4. 4. Visual/Conceptual Model:
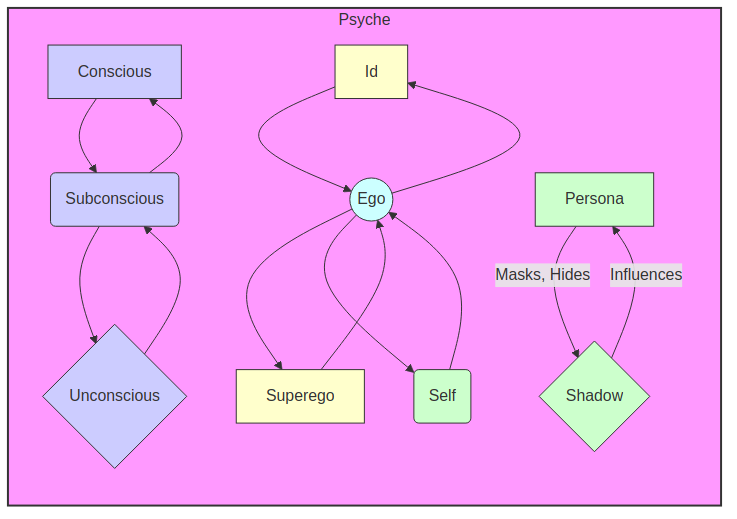
Explanation of the Model:
- The graph illustrates the relationships described above.
- Arrows indicate the direction of influence.
- The "Psyche" subgraph encompasses all components.
- The styles are merely visual aids to differentiate the components.
1.5. 5. Actionable Insights and Recommendations:
- Self-Awareness is Key: Understanding the different components of your own psyche is the first step toward personal growth. Practices like mindfulness, journaling, and therapy can help increase self-awareness.
- Address Unconscious Conflicts: Unresolved issues in the unconscious can manifest as problems in your daily life. Explore these through therapy, dream analysis, or other introspective practices.
- Integrate the Shadow: Instead of repressing your Shadow, try to understand and integrate its aspects. This can lead to greater self-acceptance and wholeness.
- Balance the Id, Ego, and Superego: Strive for a healthy balance between your desires, your conscience, and reality. Avoid being overly driven by any one component.
- Align with Your Self: The ultimate goal is to align your Ego (conscious self) with your Self (total personality). This involves living in accordance with your values and purpose.
- Continual Process: Understanding and working with the psyche is an ongoing process, not a destination. Be patient with yourself and continue to learn and grow.